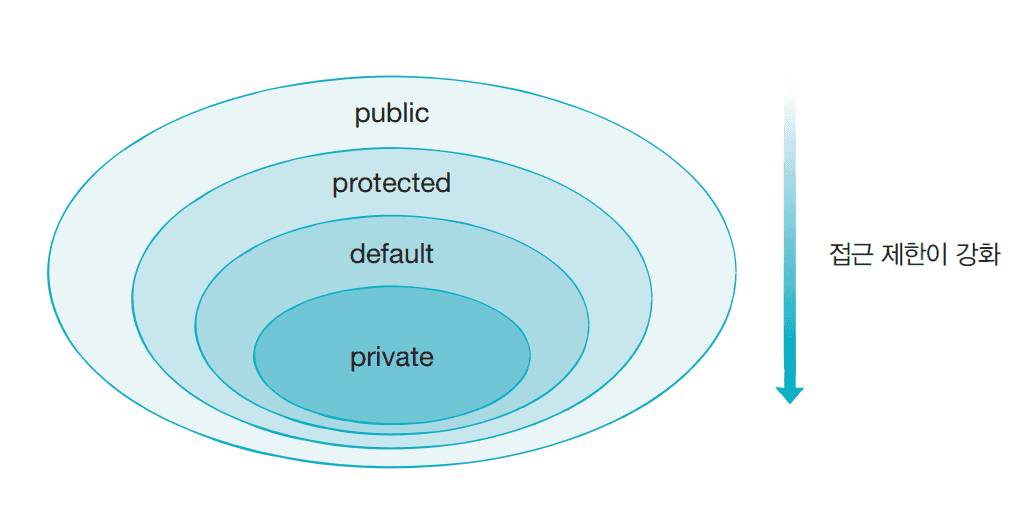
private, public, protected 접근제어
1. public : 다른 클래스에서도 접근 가능 2. private : 그 맴버를 선언한 클래스 내부에서만 접근 가능 3. protected : 그 멤버를 선언한 클래스 + 그걸 상속받은 자식 클래스 내부에서만 접근 가능
1. Public
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace @protected
{
class 아버지
{
public String 잡담 = "가족 정보";
private String 기밀 = "아주아주 중요한 맛의 비밀";
protected String 비법전수 = "자식에게만 알려주는 가문의 비법들";
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
아버지 father = new 아버지();
String 도둑;
도둑 = father.잡담;
도둑 = father.기밀; // 도둑이 애를 써도 가져갈 수 업다.
도둑 = father.비법전수; // 도둑이 애를 써도 가져갈 수 업다.
}
}
}그래서 도둑이 아버지를 납치하기로 했다. 하지만 접근하지 못하였다.
2. Private
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace @protected
{
class 아버지
{
public String 잡담 = "가족 정보";
private String 기밀 = "아주아주 중요한 맛의 비밀";
protected String 비법전수 = "자식에게만 알려주는 가문의 비법들";
}
class 도둑
{
void 함수()
{
아버지 father = new 아버지();
String a1 = father.잡담;
String a2 = father.기밀;
String a3 = father.비법전수;
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
아버지 father = new 아버지();
String 도둑;
도둑 = father.잡담;
도둑 = father.기밀;
도둑 = father.비법전수;
}
}
}그렇게 아들이 탄생하고 나서 아버지가 아들에게 비법을 상속을 했다.
Protected
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace @protected
{
class 아버지
{
public String 잡담 = "가족 정보";
private String 기밀 = "아주아주 중요한 맛의 비밀";
protected String 비법전수 = "자식에게만 알려주는 가문의 비법들";
}
class 아들 : 아버지 // 아들이 아버지를 상속받는다.
{
void 함수()
{
String a1 = 잡담;
String a2 = 기밀; // 기밀은 전달받지 못한다.
String a3 = 비법전수; // 비법전수를 상속을 받으면 열람할 수 있기 때문에 열람이 가능하다.
}
}
class 도둑
{
void 함수()
{
아버지 father = new 아버지();
String a1 = father.잡담;
String a2 = father.기밀;
String a3 = father.비법전수;
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
아버지 father = new 아버지();
String 도둑;
도둑 = father.잡담;
도둑 = father.기밀;
도둑 = father.비법전수;
}
}
}결론
- 아버지는 잡담, 기밀, 비법전수 모두 접근이 가능하고
- 아들은 잡담, 비법전수 까지 접근이 가능하고
- 도둑은 잡담 밖에 접근이 불가능하다.